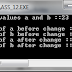
Variable
A variable is a named memory location or memory cell. It is
use to store program input data and results. The value of a variable may change
during execution of program. However, the name of variable can be changed .The
variable are created in RAM.
Variable Declaration
The process
of specifying the variable name and its data type is called variable
declaration .A variable can be declared anywhere in the program before its use.
Syntax :-
Data_type variable_name ;
Example :-
Int marks ,
sum ;
Float avg ;
Variable Initialization:-
The process
of assigning a value to a variable at the time of declaration is known as Variable initialization. The equal sign
(=) is used to initialize a variable .Variable name is written on left side and
the value is written on the right side of equal sign (=).
Syntax:-
Data_type
variable = value;
Example
int a=100 ;
Rules for naming variables in C language:
i.
Variable
may include letters, numbers and underscore (_).
Example
Int _no1 , user_age , _1 , _2 ;
ii.
The
first character of variable must be a letter or underscore _. Example (It is invalid )
int 1no , 2no ;
Example (It is Valid)
int no1 , no2 ;
iii.
Blank
spaces are not allowed in variables names.
Example
(It is invalid )
int no 1 no 2 ;
Example (It is Valid)
int no1 , no2 ;
iv.
Special
symbols cannot be used as variables names.
Example (It is invalid )
int no# , no@ , %name , _^ ;
Example (It is Valid)
int no1 , no2 ;
v.
Reserved
word/keywords cannot be used as variables names.
Example
(It is invalid )
int if , for , do , while , float
, char , pow , sqrt ,break ;
Example (It is Valid)
int no1 , no2 , ageint , nofor ,nodo ;
vi.
A
variable can be up to 31 characters long for many compilers.
vii.
A
variable can be declared only one data type.
Example
(It is invalid )
int no1, no2 ;
float avg , no1 ;
Example (It is Valid)
int no1 , no2 ;
float avg , no3 ;