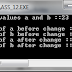
If Statement in C
If statement is used to execute a statement or set of statements, or skip this statements. The ability to control the flow of your program, letting it make decisions on what code to execute, is valuable to the programmer. The if statement allows you to control if a program enters a section of code or not based on whether a given condition is true or false. One of the important functions of the if statement is that it allows the program to select an action based upon the user's input. For example, by using an if statement to check a user-entered password, your program can decide whether a user is allowed access to the program.Without a conditional statement such as the if statement, programs would run almost the exact same way every time, always following the same sequence of function calls. If statements allow the flow of the program to be changed, which leads to more interesting code.
Syntax
Its syntax is as follows.
if(condition)
statements;
else
statements;
Two or more statements are written in curly brackets { }. The
syntax for compound statements in if
else statement is as follows:
if(condition)
{
Statements 1;
Statements 2:
.
Statements N;
}
else
{
Statements 1;
Statements 2:
.
Statements N;
}
Example
if ( 5 < 10 )
printf( "Five is less then ten" );
Here, we're just evaluating the statement, "is five less than ten", to see if
it is true or not; with any luck, it is! If you want, you can write your
own full program including stdio.h and put this in the main function and run
it to test.
To have more than one statement execute after an if statement that evaluates
to true, use braces, like we did with the body of the main function. Anything
inside braces is called a compound statement, or a block. When using if
statements, the code that depends on the if statement is called the "body" of
the if statement.
Write a program that takes marks from user via keyboard. If
marks greater 40 then display “Congratulation! You have Passed” if marks less
than 40 then display “Oops! You have Fail”.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
clrscr();
int marks;
cout<<"Enter your marks: ";
cin>>marks;
if(marks>=40)
cout<<"Congratulation! You have Passed. ";
else
cout<<"Oops! Your fail.";
getch();
}