Computer
Science (A-Course) IST/A 2014
Q.1 Write a program to finds the sum of the cubes of the
integers from 1 to n. where n is entered by user i.e. (13+23+33+43………..+n3)? (10)
Solution
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
clrscr();
int a,n;
long int cube=0;
printf("Enter the value ::");
scanf("%d",&n);
a=2;
while(a<=n)
{
cube=cube+(a*a*a);
a=a+2;
}
printf("Cube of the series is %ld",cube);
getch();
}
Q2. Write a Program
to find the greatest of three numbers; here the three values are passed to the function
which returns the greatest of three? (10)
Solution
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int function(int,int,int);
void main()
{
clrscr();
int a,b,c,r;
printf("Enter three numbers:");
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
r=function(a,b,c);
printf("Greatest number is %d",r);
getch();
}
int function(int x,int y,int z)
{
int max;
max=x;
if(max<y)
max=y;
if(max<z)
max=z;
return max;
}
Q3. Write a program
that inputs a number from 1 to 10 and display it’s in words using switch
statement. For example if user enter 6, it display “six”? (10)
Solution
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
clrscr();
int n;
printf("Enter a number from 1
to 10....::");
scanf("%d",&n);
switch(n)
{
case 1:
printf("One");
break;
case 2:
printf("Two");
break;
case 3:
printf("Three");
break;
case 4:
printf("Four");
break;
case 5:
printf("Five");
break;
case 6:
printf("Six");
break;
case 7:
printf("Seven");
break;
case 8:
printf("Eight");
break;
case 9:
printf("Nine");
case 10:
printf("Ten");
default:
printf("Invalid Choice...");
}
getch();
}
Q4.
A. What is difference between “pass by value
and pass by reference” in function? (5)
Pass by value…
A parameter
passing mechanism in which the value of actual parameter is copied to formal
parameter of called function is known as pass by value. If the function makes
any change in formal parameter, it does not affect the values of actual
parameter. It is the default mechanism for passing parameters to functions.
For example write
a program that inputs two numbers in main () function, passes these numbers a
function. The function displays the maximum number.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int
function(int,int);
void main()
{
clrscr();
int a,b;
printf("Enter
three numbers:");
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
function(a,b);
getch();
}
int function(int
x,int y)
{
if(x<y)
printf("Maximum
number is %d",x);
else
printf("Maximum
number is %d",x);
}
Pass by Reference
A parameter
passing mechanism in which the address of actual parameter is passed it the
called function is known as pass by reference. The formal parameter is not
created separately in the memory. Formal parameter becomes a second name of
actual variable parameter. It means that single memory location is shared
between actual parameter and formal parameter. If the called function makes any
change in formal parameter, the change also available in calling functions.
Write a program
that inputs two numbers in main () and passes the integer s to a function by
reference. The function swaps the values. The main () function should display
the values before and after swapping.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void swap(int
&,int&);
void main()
{
clrscr();
int a,b;
printf(“Enter an
integer…:”);
scanf(“%d”,&a);
printf(“Enter an
integer…:”);
scanf(“%d”,&b);
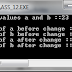
printf(“Values
before swaping\n”);
printf(“a=%d\nb=%d\n”,a,b;
swap(a,b);
printf(“Values
after swaping\n”);
printf(“a=%d\nb=%d\n”,a,b;
getch();
}
void swap(int
&x,int&v)
{
Int t;
t=x;
x=y;
y=t;
}
B. What is the difference between compiler and
interpreter? (5)
Compiler
A compiler is program
that converts the instruction of a high level language into machine language as
whole. A program that written in high level language is called source program. A compiler convert’s
source program into machine code is known as object program.
A
compiler can translate the program of only that for which it is written. For
example C compiler can translate only those program that are written in C
language.
Interpreter
An
interpreter is program that converts
one statement of program at one time. It executes this statement before
translating the next statement of the source program. If these are an error in
the statements, the interpreter stops working and display and error message.
The
advantage of interpreter over compilers is that an error is found immediately.
So the programmer can convert errors during program development.
The
disadvantage of interpreter is that it is not very efficient. The interpreter
does not produce an abject program. It must covert the program each time it is
executed. Visual Basic uses interpreter.
Q5.
A. What
are Logical Operators? (5)
Logical operators
Logical operators are used to
evaluate more than one condition in single conditional structure. The three
logical operators are AND(&&) operators,
OR (||) and NOT (!) operators.
AND Operators (&&)
AND(&&)
operators is a logical operators. It is used to determine the two or more
condition in one conditional statement. It remains true if those entire two or
more conditional is true. It remains false if one condition is false.
|
Condition 1
|
Operator
|
Condition 2
|
result
|
|
True
|
&&
|
False
|
False
|
|
True
|
&&
|
True
|
True
|
|
False
|
&&
|
True
|
False
|
|
False
|
&&
|
False
|
False
|
OR Operator(||)
It is used to determine two
or more condition used in one condition statement. It remains true if one
condition is true in the given statement. It remains false if all condition is
false.
|
Condition 1
|
Operator
|
Condition 2
|
Result
|
|
True
|
||
|
False
|
True
|
|
True
|
||
|
True
|
True
|
|
False
|
||
|
True
|
True
|
|
False
|
||
|
False
|
False
|
NOT Operator(!)
It remains true if the given
condition is false. It remains false if the given condition is true.
|
Operator
|
Condition
|
Result
|
|
!
|
False
|
True
|
|
!
|
True
|
False
|
B. What is flowchart explain different flow
chart symbols? (5)
Flowchart
Flowchart is combination
of two words i.e. flow and chart. Chart consists of different symbols to
display information about any program. Flow indicates the direction of
processing that takes place in the program. Flowchart is a graphical
representation of an algorithm. It is used to show all the steps of an algorithm
in a sequence.
Normally,
an algorithm is first converted to a flowchart to show its steps graphically.
The flowchart is then converted into a program written in ay programming
language.
Flowchart Symbols
1. Input/output
Parallelogram
symbol is used to represent an input or output step. Input statement is used to
get input from user. The output statement is used to display a message to the
user or display a value
2. Process
Rectangle symbol
is used to represent a process step. A process step may be a complex
calculation or simply an assignment statement.
|
3. Selection
Diamond symbol
is used to represent a selection step. A condition is given in the diamond. The
flow of control from diamond may go in two direction i.e. one direction if the
condition is true and the second direction if the condition is false.
4. Start/End
Oval symbol is used to represent the start or end of the flowchart
5. Flow Lines
Arrow symbols are used to represent
the direction of flow in the flowchart. There are four types of flow lines.
6. Connector
Circle symbol is
used to combine different line. It is used when two are more flow symbols come
from different direction and move to one direction.
Q6. Write a program
that inputs a number in main function and passes the number to a function. The
function display factorial of the number? (10)
Solution
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int factorial(int);
void main()
{
int n,r;
clrscr();
printf("Enter any number ::");
scanf("%d",&n);
factorial(n);
getch();
}
int factorial(int x)
{
int f,a;
f=1;
a=1;
while(a<=x)
{
f=f*a;
a++;
}
printf("The Factorial of %d is %d",x,f);
}
Q7. Write a C program
to read any character from user and if that character is capital letter then
display it with small letter and if it is small letter then display with
Capital letter. (10)
Solution.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
clrscr();
char ch;
printf("Enter Any Character....");
scanf("%c",&ch);
if(ch>='a'&&ch<='z')
ch=ch-32;
else if(ch>='A'&&ch<='Z')
ch=ch+32;
else
printf("Invalid Choice...");
printf("%c",ch);
getch();
}
Q8. Write a program
that calculate electric bill depending on the following conditions Consumption
Units Rate of charges
000 --- 200 Rs. 0.50 per unit
201 ---400 Rs. 100 plus Rs. 0.65
per unit excess of 200
401--- 600 Rs. 230 plus Rs. 0.80
per unit excess of 400
601 and above Rs. 390 plus Rs.
1.00 per unit excess 600 (10)
Solution.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
clrscr();
int bill,un,p;
printf("Enter Consumption Units....");
scanf("%d",&un);
if(un>0&&un<=200)
bill=un*0.5;
else if(un>200&&un<=400)
bill=un*0.65+100;
else if(un>400&&un<=600)
bill=un*0.80+230;
else if(un>600)
bill=un*1+390;
printf("The bill is %d",bill);
getch();
}